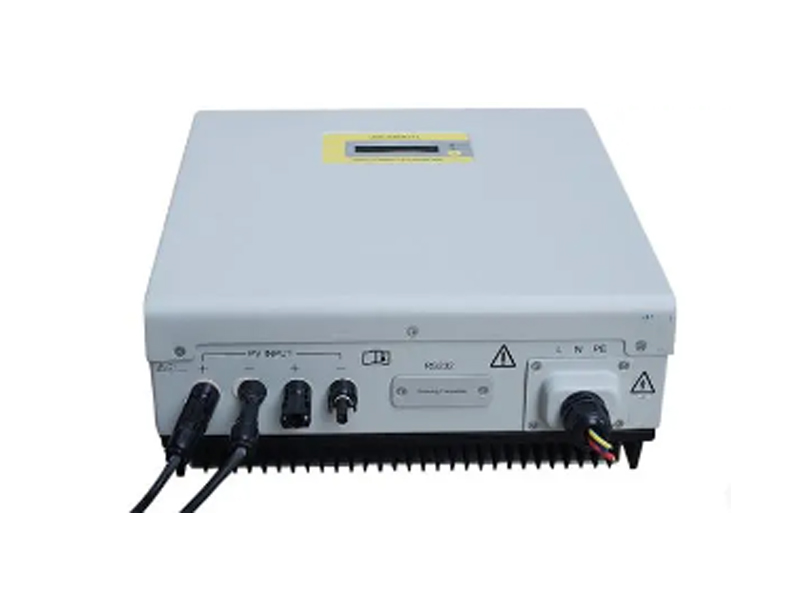
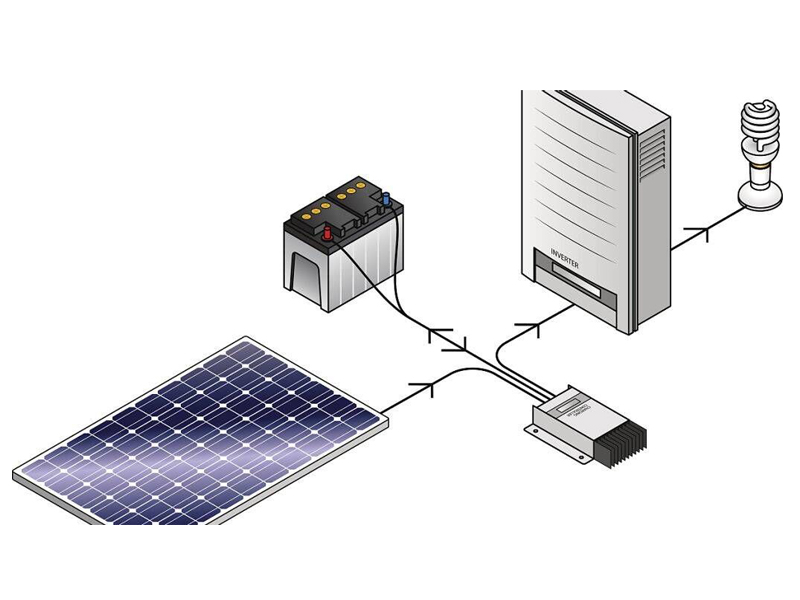
The inverter is a power adjustment device composed of semiconductor devices, which are mainly used to convert DC power into AC power. It is generally composed of a boost circuit and an inverter bridge circuit. The boost circuit boosts the DC voltage of the solar cell to the DC voltage required for the inverter output control; the inverter bridge circuit converts the boosted DC voltage into an AC voltage with a common frequency equivalently.
Inverter, also known as power regulator, can be divided into the independent power supply and grid-connected use according to the use of inverter in the photovoltaic power generation system. According to the waveform modulation method, it can be divided into square wave inverter, step wave inverter, sine wave inverter, and combined three-phase inverter. For inverters used in grid-connected systems, they can be divided into transformer-type inverters and transformer-less inverters according to whether there is a transformer. The main technical parameters of the solar photovoltaic inverter are:
1. Rated output voltage
The photovoltaic inverter should be able to output the rated voltage value within the allowable fluctuation range of the specified input DC voltage. Generally, when the rated output voltage is single-phase 220v and three-phase 380v, the voltage fluctuation deviation is specified as follows.
(1) When running in a steady state, it is generally required that the voltage fluctuation deviation does not exceed ±5% of the rated value.
(2) When the load is suddenly changed, the voltage deviation does not exceed ±10% of the rated value.
(3) Under normal working conditions, the unbalance of the three-phase voltage output by the inverter should not exceed 8%.
(4) The distortion of the voltage waveform (sine wave) of the three-phase output is generally required not to exceed 5%, and the single-phase output should not exceed 10%.
(5) The deviation of the frequency of the inverter output AC voltage should be within 1% under normal working conditions. The output voltage frequency specified in the national standard Gb/t 19064-2003 should be between 49 and 51hz.
2. Load power factor
The size of the load power factor indicates the ability of the inverter to carry an inductive load or capacitive load. Under the condition of a sine wave, the load power factor is 0.7 to 0.9, and the rated value is 0.9. In the case of certain load power, if the power factor of the inverter is low, the required capacity of the inverter will increase, resulting in an increase in cost. At the same time, the apparent power of the AC circuit of the photovoltaic system increases, and the circuit current increases. If it is large, the loss will inevitably increase, and the system efficiency will also decrease.
3. Rated output current and rated output capacity
Rated output current refers to the rated output current of the inverter within the specified load power factor range, the unit is a; rated output capacity refers to the product of rated output voltage and rated output current of the inverter when the output power factor is 1 (i.e. pure resistive load), the unit is kva or kw.
Post time: Jul-15-2022